Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography is a new imaging and diagnostic examination of the eye. It produces tomographic images of the internal structures of the retina by calculating the intensity and time delay of the reflected or diffused light, based on interferometry. It has the ability to perform high resolution scans, in the range of 1 - 15μm, resolution that is 1 to 2 orders of magnitude greater than imaging modalities such as ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Computerized Tomography. The main application of Optical Coherence Tomography to date is the imaging of the retina in Ophthalmology, but it has also been used for the display of the anterior structures of the eye as well as other tissues, such as cardiovascular, digestive, pulmonary, dental, cancer etc.
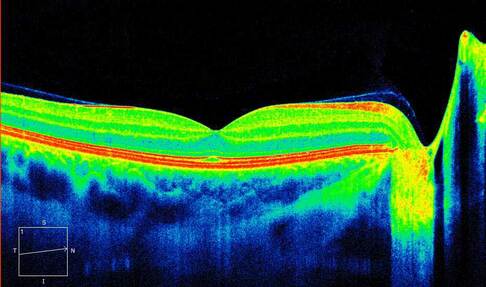
Without strict dilation of the pupil, the patient puts his head in the special instrument. Then a special set of laser light scans the retina many times and with great speed presenting almost immediately the anatomical images of the retina. The machine produces color or black and white images of the retina that help us to diagnose many diseases of the retina in a painless and quick way. This test has become indispensable to the study and monitoring of the retina and macula, replacing in many cases tests such as fluorescein angiography.
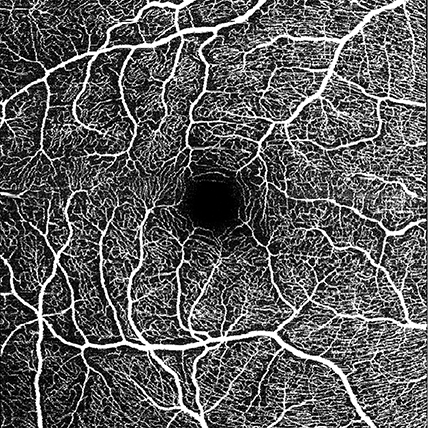
Digital OCT angiography is a recent non-invasive retinal imaging method based on the detection of blood flow in the retina and choroid by OCT scanning. This allows the visualization of the microcirculation of the retina and choroid without intravenous contrast imaging. It enables us to have a fast and detailed view of the capillary network of the posterior pole of the eye without any burden on the patient.
|
|
|
||||
The information provided in this web site is not a substitute for professional medical care by a qualified doctor or health care professional. Always check with your doctor if you have concerns about your eye condition or treatment. The authors of this web site are not responsible or liable, directly or indirectly, for any form of damages whatsoever resulting from the information contained in or implied by the information on this site. Information for patients is provided only as a guide.
Copyright Vlassis Grigoropoulos © 2020
Copyright Vlassis Grigoropoulos © 2020
Design: Vlassis Grigoropoulos
Proudly powered by Weebly






